Enhancing Buildings with Stone Veneer Facade A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction The facade of a building plays a crucial role in creating a lasting impression. It serves as the face of the structure, reflecting the style, character, and quality of the building. Stone veneer facade has gained popularity as a versatile and aesthetically pleasing option for enhancing the exterior of buildings. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various aspects of stone veneer facade, including its benefits, types, installation process, maintenance, and design considerations. Benefits of Stone Veneer Facade Stone veneer facade offers a wide range of benefits that make it a popular choice among architects, builders, and homeowners. Some of the key advantages of using stone veneer facade include: 1. Aesthetic Appeal: Stone veneer facade adds a touch of elegance and sophistication to any building. It comes in a variety of colors, textures, and patterns, allowing for endless design possibilities. 2. Durability: Stone veneer is highly durable and can withstand harsh weather conditions, making it an ideal choice for exterior applications. It is resistant to fading, cracking, and chipping, ensuring a long-lasting facade. 3. Lightweight: Unlike natural stone, which can be heavy and cumbersome to install, stone veneer is lightweight and easy to work with. This makes the installation process quicker and more cost-effective. 4. Versatility: Stone veneer can be used on a wide range of surfaces, including concrete, wood, metal, and drywall. It can be applied to both new construction projects and renovations, offering flexibility in design. 5. Cost-Effective: Stone veneer facade provides the look and feel of natural stone at a fraction of the cost. It is a cost-effective alternative to traditional stone cladding, without compromising on aesthetics or quality. Types of Stone Veneer There are several types of stone veneer available in the market, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. The most common types of stone veneer include: 1. Natural Stone Veneer: Natural stone veneer is made from real stone that has been cut into thin slices. It retains the natural color, texture, and variations of the original stone, providing an authentic look and feel. 2. Manufactured Stone Veneer: Manufactured stone veneer, also known as faux stone or cultured stone, is made from a mixture of cement, aggregates, and pigments. It is designed to mimic the appearance of natural stone, offering a more affordable and lightweight alternative. 3. Brick Veneer: Brick veneer is a type of stone veneer made from clay bricks that are cut into thin slices. It provides a classic and timeless look, reminiscent of traditional brick masonry. 4. Stacked Stone Veneer: Stacked stone veneer features irregularly shaped stones that are stacked together to create a rugged and textured appearance. It is commonly used to add a rustic or contemporary look to the facade. Installation Process The installation of stone veneer facade requires careful planning, preparation, and execution to ensure a seamless and durable finish. The following steps outline the typical installation process for stone veneer facade: 1. Surface Preparation: The surface of the building must be clean, dry, and free of any debris or contaminants before installing the stone veneer. Any existing cladding or siding should be removed, and the surface should be inspected for any structural issues. 2. Moisture Barrier: A moisture barrier, such as building paper or house wrap, should be installed over the sheathing to prevent water infiltration and protect the building from moisture damage. 3. Roofing slate installation tools needed : A metal lath is attached to the surface using galvanized nails or screws. The lath provides a secure base for the stone veneer to adhere to and helps promote proper drainage. 4. Scratch Coat Application: A scratch coat of mortar is applied to the metal lath using a trowel. The scratch coat provides a rough surface for the stone veneer to bond to and ensures a strong and durable attachment. 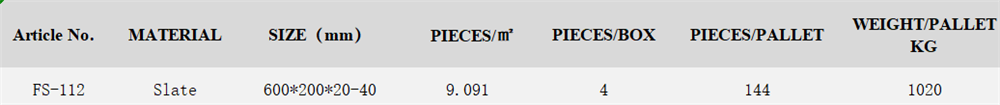 5. Stone Veneer Installation: The stone veneer pieces are carefully arranged and adhered to the scratch coat using a mortar mix. The joints between the stones are filled with mortar to create a seamless and cohesive facade. 6. Grouting and Finishing: Once the stone veneer is in place, the joints are filled with grout to enhance the appearance and durability of the facade. Any excess mortar or grout should be cleaned off the surface to achieve a clean and polished finish. Maintenance Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and beauty of a stone veneer facade. Here are some tips for maintaining a stone veneer facade: 1. Regular Cleaning: To keep your stone veneer facade looking its best, regularly clean it with a mild detergent and water. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners, as they can damage the surface of the stones. 2. Sealing: Depending on the type of stone veneer, it may be beneficial to apply a sealer to protect the facade from moisture, stains, and fading. Consult with the manufacturer or a professional for guidance on the appropriate sealer for your specific stone veneer. 3. Inspections: Periodically inspect the stone veneer facade for any signs of damage, such as cracks, chips, or loose stones. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage and maintain the integrity of the facade. 4. Repairs: If any stones become loose or damaged, repair them as soon as possible to prevent water infiltration and structural issues. Use a mortar mix that matches the color and texture of the existing stones for seamless repairs. Design Considerations When designing a stone veneer facade, there are several factors to consider to achieve a cohesive and visually appealing finish. Some design considerations for stone veneer facade include: 1. Color Palette: Choose a color palette that complements the overall aesthetic of the building and blends harmoniously with the surrounding environment. Consider the architectural style, landscaping, and color scheme of the building when selecting the stone veneer color. 2. Texture and Pattern: Experiment with different textures and patterns to create visual interest and depth in the facade. Stacked stone, brick veneer, and natural stone veneer offer a variety of textures that can enhance the facade's appearance. 3. Proportion and Scale: Ensure that the size and scale of the stone veneer pieces are proportionate to the building's size and architectural features. Large stones may overwhelm a small building, while small stones may get lost on a larger structure. 4. Integration with Other Materials: Consider how the stone veneer facade will interact with other materials used in the building, such as wood, metal, or glass. Create a cohesive and balanced design by incorporating complementary materials that enhance the overall aesthetic. Conclusion Stone veneer facade is a versatile and attractive option for enhancing the exterior of buildings. With its aesthetic appeal, durability, and versatility, stone veneer offers a wide range of benefits that make it a popular choice among architects, builders, and homeowners. By understanding the different types of stone veneer, the installation process, maintenance requirements, and design considerations, you can create a stunning and long-lasting facade that enhances the beauty and value of any building. Whether you are renovating an existing structure or designing a new construction project, stone veneer facade is a timeless and elegant choice that will make a lasting impression.
5. Stone Veneer Installation: The stone veneer pieces are carefully arranged and adhered to the scratch coat using a mortar mix. The joints between the stones are filled with mortar to create a seamless and cohesive facade. 6. Grouting and Finishing: Once the stone veneer is in place, the joints are filled with grout to enhance the appearance and durability of the facade. Any excess mortar or grout should be cleaned off the surface to achieve a clean and polished finish. Maintenance Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and beauty of a stone veneer facade. Here are some tips for maintaining a stone veneer facade: 1. Regular Cleaning: To keep your stone veneer facade looking its best, regularly clean it with a mild detergent and water. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners, as they can damage the surface of the stones. 2. Sealing: Depending on the type of stone veneer, it may be beneficial to apply a sealer to protect the facade from moisture, stains, and fading. Consult with the manufacturer or a professional for guidance on the appropriate sealer for your specific stone veneer. 3. Inspections: Periodically inspect the stone veneer facade for any signs of damage, such as cracks, chips, or loose stones. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage and maintain the integrity of the facade. 4. Repairs: If any stones become loose or damaged, repair them as soon as possible to prevent water infiltration and structural issues. Use a mortar mix that matches the color and texture of the existing stones for seamless repairs. Design Considerations When designing a stone veneer facade, there are several factors to consider to achieve a cohesive and visually appealing finish. Some design considerations for stone veneer facade include: 1. Color Palette: Choose a color palette that complements the overall aesthetic of the building and blends harmoniously with the surrounding environment. Consider the architectural style, landscaping, and color scheme of the building when selecting the stone veneer color. 2. Texture and Pattern: Experiment with different textures and patterns to create visual interest and depth in the facade. Stacked stone, brick veneer, and natural stone veneer offer a variety of textures that can enhance the facade's appearance. 3. Proportion and Scale: Ensure that the size and scale of the stone veneer pieces are proportionate to the building's size and architectural features. Large stones may overwhelm a small building, while small stones may get lost on a larger structure. 4. Integration with Other Materials: Consider how the stone veneer facade will interact with other materials used in the building, such as wood, metal, or glass. Create a cohesive and balanced design by incorporating complementary materials that enhance the overall aesthetic. Conclusion Stone veneer facade is a versatile and attractive option for enhancing the exterior of buildings. With its aesthetic appeal, durability, and versatility, stone veneer offers a wide range of benefits that make it a popular choice among architects, builders, and homeowners. By understanding the different types of stone veneer, the installation process, maintenance requirements, and design considerations, you can create a stunning and long-lasting facade that enhances the beauty and value of any building. Whether you are renovating an existing structure or designing a new construction project, stone veneer facade is a timeless and elegant choice that will make a lasting impression.